Debt-to-Income Ratio: What It Is, Calculating It, and How to Improve It
Your debt-to-income ratio is one of the key factors lenders use to decide whether you can afford to take on more debt and make another monthly payment. A good debt-to-income ratio can make the difference between being approved or declined for credit, so it’s essential to know yours and, if necessary, take steps to improve it.

What is debt-to-income ratio?
Debt-to-income ratio (sometimes called DTI ratio) is one of many factors that lenders use to evaluate your ability to manage your debt and your monthly payments. Debt-to-income ratio is a measure of how much you owe each month compared to how much you earn. The lower your debt-to-income ratio, the less risky you appear to lenders. A higher debt-to-income ratio suggests that you might be overextended and would have a hard time repaying additional debt.
How to calculate debt-to-income ratio
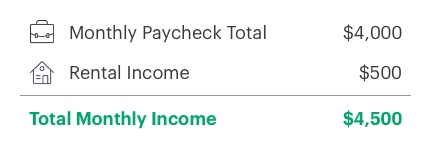
Calculating your debt-to-income ratio is simple. First, add up all your monthly debt bills (such as a car payment, rent or housing payment, and credit card payments). Next, divide that number by your total monthly income before taxes. The result is a percentage known as your debt-to-income ratio. Here’s an example:
Debt payments

Income

Where do lenders get the information to determine your debt-to-income ratio?
Most debt information can be found on your credit report, but many lenders will also ask you for some (or all) of your debt payment information as part of their application process. Since your income is not included on your credit report, almost every lender will ask for your self-reported income. Paycheck and W-2s are good documents to use for verification, so be prepared to submit these to lenders when applying for credit.
How do lenders use debt-to-income ratio?
Lenders use debt-to-income ratio to gauge how well you’ll be able to handle additional debt and debt payments. The lower your debt-to-income ratio, the less risky you appear to potential lenders and the more likely you are to be approved. If a lender doesn’t think you can handle more debt, they may deny credit to you altogether, or they may only offer you a small amount of money that they think you’ll be able to repay.
Even though your debt-to-income ratio is not found directly on your credit report, it is an important factor that impacts your ability to secure credit, like a car loan or mortgage. Focusing on improving your debt-to-income can help you gain access to affordable credit in the future. Learn more about what else lenders use to evaluate applicants beyond your credit report.
What is a good debt-to-income ratio?
Different loan products and lenders will have different DTI limits, so there’s no magic number. For example, most mortgage lenders want to see a DTI below 36%; however, it’s still possible, depending on the lender, to get a mortgage with a DTI over 40%. That said, the lower your debt-to-income ratio is, the better.
How to improve your debt-to-income ratio
There are two ways to lower your debt-to-income ratio: lower your debt or increase your income.
For most of us, increasing our income is easier said than done. If a high debt-to-income ratio is preventing you from getting access to credit that you need, some lenders may allow you to apply with a co-applicant or add a co-signer to your loan and have that person’s income considered as part of your application. Although this may help you get approved for credit, it won’t actually lower your personal debt-to-income ratio.
The other way to improve your debt-to-income ratio is to decrease your debt. Use these 3 tips to tackle a high DTI ratio:
- Stop taking on more debt. Don’t apply for new credit, avoid running up your credit card balances, and hold off on any major purchases.
- Pay down existing debt. Evaluate different strategies for paying down your debt. For example, you might be able to streamline and lower your monthly debt payments with a debt consolidation loan, or you may be able to temporarily save on your monthly credit card bill with a balance transfer offer.
- Reduce your spending for the long term. Revisit your budget to figure out where your money is going each month. Try some of these budgeting apps if you need a little extra help. Consider getting into better money habits and avoid overspending. Use any remaining money you have each month to make extra payments on your existing debts.
Bottom Line
Your debt-to-income ratio is not included in your credit report or your credit score, but it’s a key financial health indicator that shows lenders if you’re living within your means. And, if you have a high DTI ratio you might also have a high credit utilization ratio, which does have a major influence on your credit score. Monitor your credit score for free and get credit education tools on Upgrade Credit Health Monitoring.


